How to Cut Plastic: A Better Way with Ultrasonic Cutting Technology
Publish Data:2025.7.30 Author: Hyusonic
Introduction: The Challenges of Cutting Plastic
Cutting plastic is a common task across industries, from manufacturing and prototyping to DIY projects. However, anyone who has tried to cut plastic knows it’s not always easy. Hard plastics can crack or chip. Thin sheets may melt or warp. Even the best traditional tools can leave rough edges or create safety hazards.
When cutting plastic, factors like the type of plastic (ABS, acrylic, PVC, HDPE), thickness, and shape of the material all play a critical role. Choosing the wrong cutting method can result in poor product quality, wasted materials, and potential safety risks.
This article explores how ultrasonic cutting technology offers a cleaner, faster, and more precise alternative to traditional plastic cutting methods.

Traditional Cutting Methods: Pros and Cons
1. Manual Sawing
Hand saws or hacksaws are often used for thicker plastics. While affordable and easy to find, they can be time-consuming and produce jagged edges.
Pros:
Cheap and accessible
Suitable for basic DIY tasks
Cons:
Requires force
Often results in rough edges
Not ideal for precision work
2. Rotary Tools (e.g., Dremel)
Rotary tools can cut thin plastic sheets and small parts. They offer more control than hand saws but still generate a lot of heat.
Pros:
Good for small, intricate cuts
Versatile for other materials
Cons:
Can melt plastic
Generates dust and debris
3. Laser Cutting
Laser cutters offer clean cuts and automation but come with a high cost and can emit toxic fumes when cutting certain plastics.
Pros:
Precise and programmable
Smooth finishes
Cons:
Expensive
Not safe for all plastic types (e.g., PVC)
4. Hot Knife
A heated blade that melts its way through plastic. It can cut soft plastics but lacks clean edges and control.
Pros:
Quick for thin or soft plastic
Cons:
Leaves melted edges
Not suitable for clean, precise cuts
What is Ultrasonic Plastic Cutting?
Ultrasonic cutting uses high-frequency vibration (typically 20-40 kHz) to create friction at the molecular level. This friction melts a thin layer of the plastic at the cutting point, allowing the blade to glide through the material without resistance.
The blade does not rely on sharpness or high pressure. Instead, the vibration does the work, making it ideal for cutting a wide range of thermoplastic materials.
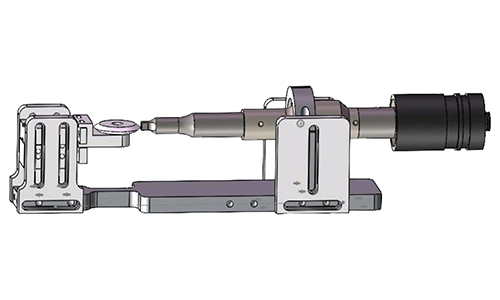
Why Use an Ultrasonic Cutter for Plastic?
1. Smooth, Burr-Free Edges
Unlike saws or hot knives, ultrasonic cutters leave clean, sealed edges with no burrs, chips, or melting residue.
2. No Cracking or Warping
Because the ultrasonic cutter uses low mechanical force and minimal heat, it prevents warping or cracking, especially in hard plastics like ABS or acrylic.
3. Precision for Complex Shapes
The fine control of ultrasonic cutting makes it perfect for detailed patterns, curves, and tight tolerances that traditional tools struggle with.
4. Cleaner Work Environment
Ultrasonic cutting generates less dust, debris, and odor. There’s no smoke or harmful fumes compared to laser or rotary cutting.
5. Increased Safety
Operators are less likely to experience injuries due to the non-rotating, low-pressure nature of ultrasonic tools.
Application Examples: Cutting Different Types of Plastic
1. How to Cut Hard Plastic (e.g., ABS, Acrylic)
Hard plastics are prone to cracking under stress. Ultrasonic cutters avoid mechanical stress by melting a fine line as they pass, allowing a smooth and stress-free cut.
Typical applications:
Consumer electronics casings
Automotive interior components
DIY enclosures and models
2. How to Cut Thick Plastic Sheets (e.g., HDPE, PVC)
Thicker plastics often require more power and precision. Ultrasonic blades can be customized for deeper penetration while maintaining clean edges.
Typical applications:
Industrial panels
Plastic piping
Heavy-duty packaging
3. How to Cut Corrugated Plastic (e.g., PP sheets, signage material)
Corrugated plastic can easily tear or fray when using traditional tools. Ultrasonic cutting ensures neat edges without crushing the internal structure.
Typical applications:
Sign boards
Storage boxes
Packaging dividers
Case Study: Cutting ABS Plastic Sheet with Ultrasonic Cutter
Challenge: A customer needed to cut 5mm thick ABS sheets into intricate shapes for an automotive dashboard. Traditional methods caused edge burning and inconsistent sizes.
Solution: Hyusonic’s ultrasonic cutter with a custom blade and 20kHz transducer delivered precise cuts with no edge damage, improving output consistency and reducing rework.
Result:
35% faster production speed
50% reduction in material waste
Cleaner, more professional product finish
Which Ultrasonic Cutter Should You Choose?
At Hyusonic, we offer a range of ultrasonic cutting systems for plastic processing:
Handheld Ultrasonic Cutter: Ideal for manual precision work, prototypes, and repair tasks.
Automated Ultrasonic Cutting System: Best for production lines requiring consistent, high-volume output.
Custom Blade Configurations: Tailored for specific material thicknesses and edge profiles.
All our ultrasonic cutters are CE and ISO9001 certified, with options for adjustable amplitude, frequency tracking, and multi-axis automation.
Ultrasonic Cutting vs. Traditional Cutting: Quick Comparison
| Feature | Ultrasonic Cutting | Traditional Cutting |
|---|---|---|
| Edge Quality | Smooth, burr-free | Often rough or melted |
| Material Damage | Minimal | High (cracks, burns) |
| Safety | High | Medium to low |
| Speed | Fast, continuous | Varies |
| Noise & Dust | Low | High |
| Precision | Excellent | Moderate to low |
FAQs
Q1: Can ultrasonic cutters cut plastic at high volumes?
Yes. Ultrasonic cutters can be integrated into automated systems for high-speed, continuous cutting.
Q2: What types of plastic can be cut with ultrasonic technology?
Common plastics include ABS, PP, PE, PVC, PET, HDPE, and polycarbonate, as long as they are thermoplastics.
Q3: Is ultrasonic cutting safe for operators?
Yes. It is safer than saws or hot knives, with no rotating parts or exposed blades during operation.
Q4: Does ultrasonic cutting produce fumes or melting?
Minimal heat is generated, and there’s no burning or harmful fumes like in laser cutting.
Q5: How thick of a plastic sheet can ultrasonic cutters handle?
Depending on the model, ultrasonic cutters can handle plastics up to 10mm thick or more with proper blade configuration.
Conclusion
If you’re wondering how to cut plastic efficiently, safely, and with professional results, ultrasonic cutting technology is the answer. It outperforms traditional tools in nearly every aspect—precision, cleanliness, speed, and versatility.
Whether you’re working with hard plastic, thick plastic sheets, or corrugated plastic, an ultrasonic cutter offers a superior solution that reduces waste and improves quality.
