What is energy director in ultrasonic welding?
Energy directors are one of the most widely used joint designs in ultrasonic plastic welding, especially for achieving high-strength, clean joints in thermoplastics.
An ultrasonic energy director is a precision-engineered welding component with triangular/trapezoidal/semi-circular protrusions on faying surfaces. It uses stress concentration to focus ultrasonic energy for controlled thermoplastic fusion. Key parameters (height 0.1–1 mm, angle 45°–60°, layout) require optimization based on material rheology, part geometry, and process dynamics. The goal is to create a small, concentrated melt zone to achieve a strong weld in a very short time. This design is crucial for achieving consistent and reliable weld quality in mass production.
Design Guide of energy director ultrasonic welding
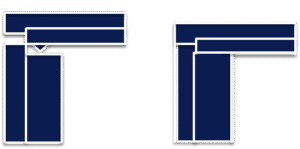
Design of Ultrasonic Energy Director
The energy director in ultrasonic welding is the protruding part on the welding surface between the two welding parts. The design of this protrusion is critical for the success of the weld.
The angle of the energy-directing protrusion is usually between 45° and 120°. The smaller the angle, the less ultrasonic energy is needed for welding. It is usually used for semi-crystalline plastics (such as PE, PA, PP and PPS) and amorphous plastics with high melting temperatures (such as PC and PSU). The larger the angle, the more suitable it is for resins that are easy to weld (amorphous plastics, such as ABS, PMMA and PS).
For example, many engineers ask: what is the optimal energy director size for ABS or PC? While ABS allows wider angles (90°–120°), semi-crystalline materials like PP often require sharper tips (45°–60°) for efficient energy absorption. These guidelines are based on the material’s melting behavior; semi-crystalline materials have a narrower melting range and require a more focused energy input to initiate the melt, while amorphous plastics melt more gradually.
Dimensional optimization of the energy director height is critical because: 1. Energy concentration mechanism. At a fixed angle, increasing the height increases the volume, thereby reducing energy concentration at the joint interface and the efficiency of ultrasonic energy transmission. 2. Melt volume control. The height of the director directly determines the volume of melted plastic that flows into the joint. An excessively high director can lead to excessive flash, while a low director may not provide enough material for a complete weld. Therefore, the optimal height must be carefully balanced to ensure a full joint without creating a mess.
Material Specific Considerations
The specified size range is designed to accommodate the different melting characteristics of plastic materials and maintain the best energy director quality for efficient welding. This means there is no one-size-fits-all solution; each material and joint design requires specific analysis and testing to find the optimal parameters. Factors like material thickness and part tolerances also influence the final design choices.
Function Of Energy Director Ultrasonic Welding
Geometric Energy Focusing
Ultrasonic vibrations concentrate stress at the tip/edge of the energy director (small cross-section, high curvature), elevating local energy density above surrounding areas. This geometric stress concentration is the fundamental principle behind the energy director’s effectiveness.
Energy Efficiency Enhancement
Minimizes energy diffusion to non-welding zones, focusing >80% of ultrasonic energy at the interface to shorten welding time (0.5–2s). This not only improves production speed but also reduces the overall thermal stress on the plastic parts, which helps maintain the material’s structural integrity.
Material & Process Adaptation
For dissimilar plastics (e.g., PA/PP), positions the director on the high-melting side to compensate for melting point differences. Accommodates rough surfaces/tolerances by ensuring initial energy transfer, reducing reliance on assembly precision. This flexibility is a major reason why energy directors are so popular in industrial applications where perfect part-to-part fit-up is not always feasible.
Joint Strength & Sealing
Concentrated melting boosts joint tensile strength to 80–90% of the base material, ensuring hermetic seals. This makes energy director welds ideal for plastic enclosures, electronic housings, and waterproof components. The uniform melt flow created by a well-designed energy director minimizes air pockets and voids, which are common causes of weak joints.
Defect Control
Optimized director height (≤0.5mm) with aesthetic seams controls melt flow, minimizing flash and improving appearance qualification rate. By precisely controlling the melt volume and flow, the energy director helps prevent flash from extruding to the part’s visible surfaces, which is critical for products where appearance is as important as functionality.


Application of Energy Director Ultrasonic Welding
Electronics: For PP+ABS welding of mobile phone casings and battery boxes, energy directors ensure rapid sealing of thin-walled structures (thickness ≤1.5mm). The precision of the energy director is vital for preventing damage to sensitive internal components during welding.
Medical Devices: In PVC welding of syringes and dialyzers, energy directors precisely control melt volume to prevent hazardous substances from material degradation. This ensures the sterility and biocompatibility of the final product, a non-negotiable requirement in the medical field.
Automotive Industry: For PC welding of dashboards and vehicle lights, energy director designs adapt to curved-surface welding, enhancing joint vibration resistance. This is essential for parts that must withstand the harsh conditions and vibrations of a vehicle’s operating environment.
Consumer Goods: For household appliances like plastic kettles or coffee makers, energy directors are used for welding plastic tanks and housings, ensuring they are watertight and durable for daily use.
