What is Ultrasonic Welding?
Ultrasonic welding is a fast, efficient, and clean joining process that uses high-frequency vibrations to generate localized heat, bonding materials together without the need for adhesives, fasteners, or external heat. The process is especially effective for welding plastics, thermoplastics, and even certain metals.
How Strong Is Ultrasonic Welding?
Ultrasonic welding delivers exceptional strength due to its precision and adaptability across various industries.
Welding Precision: The welding process can be controlled with an accuracy of up to 0.01mm, ensuring minimal damage to surrounding areas.
Speed and Efficiency: It allows for rapid welding, typically taking less than 1 second per weld, making it ideal for high-volume production.
Environmental Benefits: Unlike traditional welding, ultrasonic welding doesn’t require additional heat or chemicals, which makes it environmentally friendly.
The welding strength is similar to the base material, meaning the bond is just as strong as the material itself, ensuring reliability in high-demand applications.
What is the Disadvantage of Ultrasonic Welding?
While ultrasonic welding is efficient, it has some limitations:
Material Limitations: It works best with certain thermoplastics and non-ferrous metals. Some materials, like high-density plastics or thicker metal sheets, may not be suitable for ultrasonic welding.
High Initial Equipment Cost: The machines and setup required for ultrasonic welding can be costly, especially for industries looking to scale production.
Noise: Ultrasonic welders produce loud noise during operation, which may require hearing protection in a production environment.
Why Ultrasonic Welding Is So Strong
Energy Directors: Designed features (e.g., triangular or semi-circular ridges) concentrate vibration to initiate melting precisely, improving weld quality.
Controlled Parameters: Welding strength depends on proper tuning of amplitude, power, pressure, and time, with amplitude usually the most critical factor.
Microstructural Bonding: In metals, ultrasonic vibrations cause plastic deformation, microstructural recrystallization, and mechanical interlocking at the interface
What Materials Can Be Ultrasonically Welded?
Ultrasonic welding is versatile and can be used for various materials, including:
Plastics: Common thermoplastics such as ABS, PVC, PP, PE, PC, and PMMA.
Metals: Certain non-ferrous metals, like aluminum, copper, and brass, can also be welded using ultrasonic techniques.
Composites: Ultrasonic welding is increasingly used for joining plastic composites and even in applications involving plastics to metals (e.g., plastic-to-metal riveting or nut embedding).
What is Ultrasonic Welding Process?
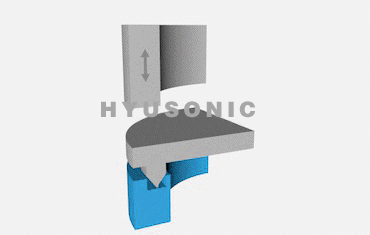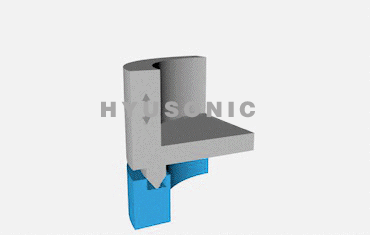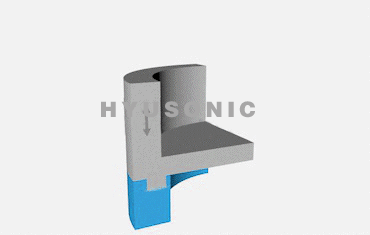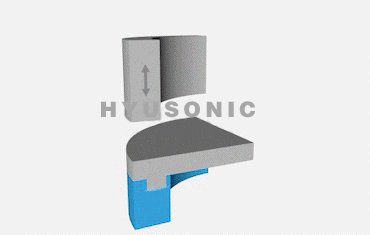
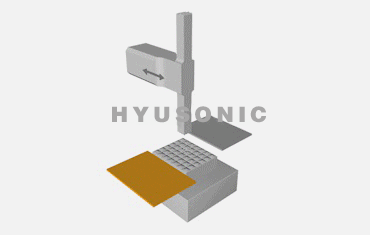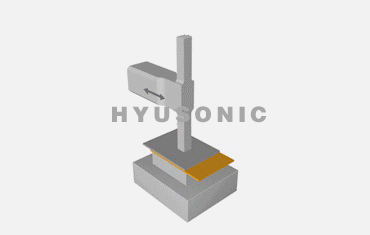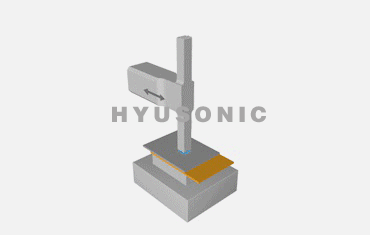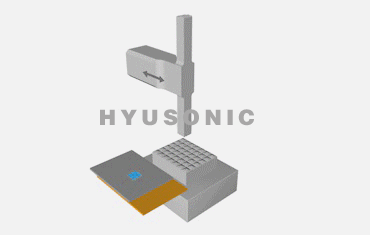
Ultrasonic welding involves a few key steps:
Power Generation: The ultrasonic generator converts 50Hz/60Hz electrical power into a high-frequency ultrasonic signal.
Energy Conversion: The ultrasonic transducer uses piezoelectric ceramics to convert electrical energy into mechanical vibrations.
Welding Action: The ultrasonic welding horn focuses the vibrations onto the materials to create a localized high-temperature zone, causing the materials to bond.
Plastic Ultrasonic Welding Process
For plastics, the material is heated through high-frequency friction to reach the glass transition temperature, allowing the molecular chains to slide and recombine. This process ensures a strong bond without melting the entire material.
Metal Ultrasonic Welding Process
In metal welding, ultrasonic vibrations create pressure between metal parts, causing atomic diffusion bonding. Unlike traditional welding, no melting occurs, making it ideal for highly conductive materials like copper and aluminum.
Is Ultrasonic Welding Loud?
Yes, ultrasonic welding produces loud noises, usually in the range of 80–100 decibels during operation. This is caused by the high-frequency vibrations used in the process. In industrial settings, workers may need to use hearing protection to mitigate the noise levels.
Advantages of Ultrasonic Welding
High Speed: The welding process typically takes less than 1 second, making it ideal for high-volume manufacturing.
Strong Bonds: The welded materials exhibit strength comparable to the original materials themselves.
Excellent Sealing: The process ensures airtight and watertight seals, which are crucial for industries like electronics, medical devices, and packaging.
Applications & Industrial Use Cases
Automotive: Wiring harnesses, battery components, plastic panels.
Medical Devices: Virus‑free sealing for IV tubing, masks, sterile packaging.
Electronics: Chip assembly, wire bonding, sensor packaging.
Packaging: Hermetic seals for blister packs, food containers, films .
The wearable device from a certain brand utilizes Hyusonic’s iQ series equipment to achieve an IP68 waterproof rating, flawless panel welds with zero traces, and a 100% joint success rate. Customer feedback indicates a 37% increase in production line efficiency and an annual savings of approximately \$560,000.
Conclusion
Ultrasonic welding is a powerful, efficient, and versatile process for joining plastics, metals, and composites. While it has some limitations, particularly in terms of noise and material types, its speed, strength, and environmental benefits make it an attractive solution for industries looking for high-quality, clean welds.