Ultrasonic vs Resistance Welding: Which Is Better?
Publish Data:2025.7.30 Author: Hyusonic
Introduction
When it comes to joining metal parts, ultrasonic welding and resistance welding are two prominent non-fusion techniques widely used across various industries. Both methods offer unique benefits and limitations depending on the application. This article will explore the fundamental differences between ultrasonic metal welding and electric resistance welding, comparing them in terms of working principles, materials, energy consumption, strength, precision, and cost. Whether you’re in the automotive, electronics, battery, or metal fabrication industry, understanding these technologies will help you choose the right welding solution for your needs.
What Is Ultrasonic Metal Welding?
Ultrasonic welding is a solid-state welding technique that uses high-frequency ultrasonic vibrations to create friction and heat between two metal surfaces under pressure. Unlike traditional fusion welding, it does not require melting or filler materials.
In ultrasonic metal welding, a sonotrode (horn) transmits vibrations at 20–40 kHz into the metals being joined. These vibrations disrupt the surface oxides and enable the atoms of the metal surfaces to bond at a molecular level. The result is a clean, fast, and highly precise weld, ideal for thin and dissimilar metals.
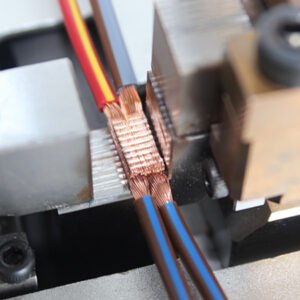
What Is Resistance Welding?
Resistance welding—more specifically electric resistance welding (ERW)—is a technique that joins metal pieces by passing an electrical current through them while applying pressure. The heat generated by the resistance of the metals to the current causes localized melting and fusion at the interface.
There are several types of resistance welding:
Spot welding (commonly used in automotive manufacturing)
Seam welding
Projection welding
Flash welding
This method is widely used for joining sheet metals, especially in high-volume production settings.

Key Differences Between Ultrasonic and Resistance Welding
| Feature | Ultrasonic Welding | Resistance Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Welding Mechanism | Friction via ultrasonic vibration (solid-state) | Joule heating via electric current (fusion) |
| Heat Input | Minimal, localized | High, localized melting |
| Material Compatibility | Ideal for dissimilar and thin non-ferrous metals (e.g., copper, aluminum) | Best for similar metals like steel |
| Weld Strength | High for small components | Moderate to high depending on parameters |
| Cycle Time | <1 second | 1–2 seconds |
| Energy Efficiency | High | Moderate |
| Precision | Very high | Moderate |
| Fume/Spatter | None | May generate sparks or fumes |
| Tool Wear | Low | Moderate to high |
| Automation | Easy to automate | Also easy to automate |
| Common Applications | Battery tab welding, foil welding, wire splicing | Automotive panels, appliance manufacturing |
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Ultrasonic Welding Applications
Battery manufacturing (e.g., lithium-ion battery tabs and busbars)
Microelectronics
Medical devices
Copper and aluminum foil welding
Solar panel assembly
Because ultrasonic metal welding doesn’t melt the material, it’s especially favored in sensitive electronic applications.
Resistance Welding Applications
Automotive body panels
Steel pipe and tubing production
Appliance manufacturing
Metal furniture frames
Steel mesh or grid structures
ERW is particularly useful when welding thicker steel sheets where structural strength is a priority.
Advantages of Ultrasonic Welding
No melting or filler required – Preserves material integrity.
Fast and repeatable – Especially in automation lines.
Low energy consumption – More sustainable manufacturing.
Minimal deformation – Critical for thin or sensitive parts.
Capable of welding dissimilar metals – Such as copper to aluminum.
Advantages of Resistance Welding
High-speed production – Great for mass manufacturing.
Strong welds on thicker metals – Especially steel.
Mature technology – Proven reliability across industries.
Well-suited for sheet metal – With excellent repeatability.
Limitations
Ultrasonic Welding:
Not suitable for thick metals (>3mm)
Requires clean contact surfaces
Higher initial equipment cost
Resistance Welding:
Generates high heat and deformation
Not ideal for very thin or delicate components
Struggles with dissimilar metals
Which One Is Better?
It depends on your application.
Choose ultrasonic metal welding if:
You work with non-ferrous and thin metals like copper or aluminum
You need precision and cleanliness
Your product involves electronics, batteries, or fine assemblies
Choose resistance welding if:
You work with thicker steel sheets
You need to join large components
You’re producing in high volumes with cost sensitivity
If you’re in the battery, wire harness, or micro-component sector, ultrasonic welding offers superior quality and speed. But for structural metal joining, resistance welding still dominates due to its simplicity and strength.
Ultrasonic vs Resistance Welding – Quick Comparison Summary
| Criteria | Best Choice |
|---|---|
| Thin metals (≤2mm) | Ultrasonic |
| Thick metals (>2mm) | Resistance |
| Dissimilar metals | Ultrasonic |
| Mass production of steel parts | Resistance |
| Minimal heat and deformation | Ultrasonic |
| Structural welds | Resistance |
| Electronics or battery use | Ultrasonic |
Future Trends in Metal Welding
As industries aim for more energy-efficient, lightweight, and precise manufacturing, ultrasonic welding is gaining traction in fields traditionally dominated by resistance welding. Innovations in ultrasonic metal welding machines are making them more accessible, customizable, and robust for industrial use.
On the other hand, electric resistance welding continues to evolve with improved electrode materials, real-time monitoring systems, and AI-based quality control.
Conclusion
Both ultrasonic welding and resistance welding have their place in modern metalworking. The decision should be based on material type, thickness, weld strength requirements, and production scale.

Whether you’re upgrading your production line or prototyping a new product, we’re here to help you choose the right welding solution.
