Heat Staking vs Ultrasonic Welding
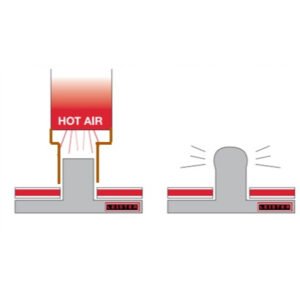
Difference of the working process principle
What is heat staking?
Heat Staking is a joining process that involves heating a plastic stud (or boss) using an external heat source, then applying pressure to melt and deform it. As the material cools and solidifies, it creates a permanent mechanical bond between components.
This technique is commonly used to assemble plastic parts, attach metal inserts, or secure components without additional fasteners like screws or adhesives. The process relies on the thermoplastic properties of the material, allowing it to soften under heat and harden when cooled, forming a reliable connection.
Ultrasonic staking utilizes the high-frequency vibration of an ultrasonic horn to generate frictional heat in plastic parts through vibration, while applying pressure to fix them, thus completing the joining of materials.
This process works by converting electrical energy into mechanical vibrations (typically at 20–40 kHz). The ultrasonic horn transfers these vibrations to the plastic stud or boss, causing molecular friction at the contact surface to raise the temperature and melt the material. Simultaneous pressure deforms the molten plastic (e.g., forming a dome or flange), which solidifies upon cooling to create a secure mechanical bond.
Difference of application
Ultrasonic staking employs a specially designed, high-precision horn that focuses vibrational energy directly onto the plastic stud, minimizing heat transfer to adjacent components. This precision ensures minimal thermal damage to sensitive parts or nearby materials.
In contrast, heat staking relies on external heat sources (e.g., heated tips or plates) to melt the plastic, which inherently involves broader thermal diffusion. This method is less precise and carries a higher risk of damaging adjacent components due to prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures.
How to choose suitable craftsmanship?
When to choose Heat Staking:
High melting-point materials (e.g., PC, PA) or temperature-insensitive plastics.
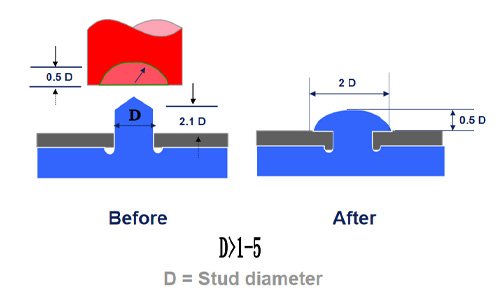
Large riveting areas (e.g., diameter >5mm) or complex geometries.
Budget constraints or low-volume production runs.
When to choose Ultrasonic Staking:
High-speed production (e.g., electronics assembly lines).
Ultra-precision requirements (e.g., medical devices).
Thin-walled components or heat-sensitive plastics (e.g., ABS thin shells).
Hyusonic are a professional manufacturer of ultrasonic welding machines and hot plate hot melt welding machines with 20 years of industry experience. We have many years of research experience in material research and welding solutions for plastics and metals. Contact us to learn about ultrasonic welding machines or heat staking machines.

