ultrasonic transducers/converters
High-efficiency ultrasonic transducers convert electrical energy into mechanical vibrations for reliable welding performance. Made with PZT-8 piezoelectric ceramics, our converters achieve >95% energy conversion efficiency with minimal heat generation. Available in 15kHz, 20kHz, 30kHz, and 40kHz frequencies, compatible.
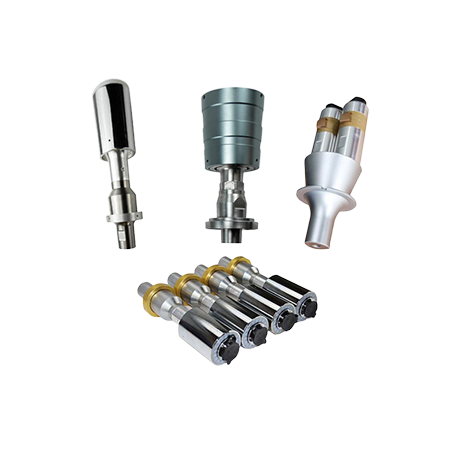

Technical Specifications
| Frequency Range | 15kHz, 20kHz, 30kHz, 35 kHz, 40kHz |
|---|---|
| Power Capacity | 400W – 5000W |
| Material | PZT-8 Ceramic, Titanium Endcap |
| Waterproof Rating | IP67 (optional IP68) |
Structural Differences of Transducer
| Feature | Hard Joint Transducer | Soft Joint Transducer |
|---|---|---|
| Connection | Rigid (threaded/flange) | Elastic (silicone/rubber buffer) |
| Vibration Transfer | Direct, minimal energy loss | Indirect via flexible medium |
| Materials | Titanium/steel threads | Silicone gaskets + metal adapter |
Design Structure
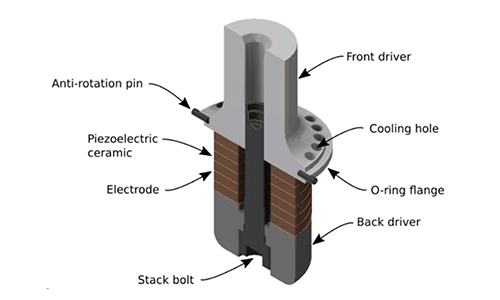
Ultrasonic transducers mainly consist of key components such as piezoelectric ceramic plates, electrode sheets, and front/rear covers.
Electro-acoustic matching: The contact surface between the electrode sheet and piezoelectric ceramic must be smooth and conductive to minimize resistive heat loss.
Mechanical resonance: The mass of the rear cover and the thickness of the front cover need to be optimized through finite element analysis to ensure the precise resonance frequency of the transducer.
Heat dissipation design: High-power transducers require integrated heat dissipation grooves on the front or rear covers to prevent the piezoelectric ceramics from depoling due to overheating (failure occurs when the Curie temperature is exceeded).
Application Guidelines
Choose Hard Joint for:
✅ Plastic welding (amplitude consistency)
✅ Metal spot welding (rigid support required)Choose Soft Joint for:
✅ Fragile materials (glass/ceramics damping)
✅ Handheld devices (reduces operator fatigue)
Customer FAQs
How does an ultrasonic welding system work?
Ultrasonic welding uses high-frequency vibrations (15-40kHz) to create friction heat between materials, bonding them in 0.1-3 seconds without adhesives. Key components:
✔ Generator – Converts electricity to high-frequency signals
✔ Transducer – Transforms electrical energy into mechanical vibrations
✔ Booster & Horn – Amplifies and directs energy to the weld area
How to test ultrasonic transducer resonance?
Use an LCR meter at 1V AC: Minimum impedance point = resonant frequency.
How often should I replace an ultrasonic transducer?
Typical lifespan:
• Standard use: 50 million cycles (~3-5 years)
• High-load use: 20 million cycles (~1.5 years)
→ Check for frequency drift >±50Hz or cracked ceramics.
Why is my transducer overheating?
Possible causes: Frequency mismatch, overload, poor cooling, or aging components. Check impedance and cooling first.
Can I replace just the piezoelectric ceramic?
Yes, if the housing is intact. Ensure the new ceramic matches the original specs (frequency, dimensions, electrode type) for proper performance.
